Computer Organization and Design 笔记 - Multicores, Multiprocessors, and Clusters
Introduction
multiprocessor
A computer system with at least two processors. This is in contrast to a uniprocessor , which has one.
job-level parallelism or process-level parallelism
Utilizing multiple processors by running independent programs simultaneously.
parallel processing program
A single program that runs on multiple processors simultaneously.
cluster
A set of compters connected over a local area network (LAN) that functions as a single large message-passing multiprocessor.
multicore microprocessor
A microprocessor containing multiple processors ("cores") in a single integrated circuit.
The Difficulty of Creating Paralel Processing Programs
According to Amdahl's law
Execution time after improvement = Execution time affected by improvement / Amount of improvement + Execution time unaffected.
Thus, \($ Speed-up = \frac{1}{(1 - Fraction~time~affected) + \frac{Fraction~time~affected}{100}}\)$
Strong scaling
Speed-up achieved on a multiprocessor without increasing the size of problem.
Weak scaling
Speed-up achieved on a multiprocessor while increasing the size of the problem proportionally to the increase in the number of processors.
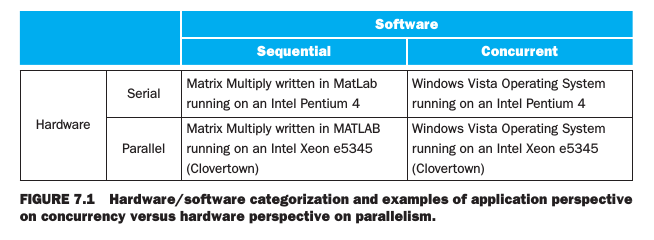
Shared Memory Multiprocessors
shared memory multiprocessor (SMP)
A parallel processor with a single address space, implying implicit communication with loads and stores.
Single address space multiplrocessors come in two styles:
- uniform memory access (UMA) : A multiprocessor in which accesses to main memory take about the same amount of time no matter which processor requets the access and no matter which word is asked.
- nonuniform memory access (NUMA) : A type of single address space multiprocessor in which some memory accesses are much faster than others depending on which processor asks for which word.
Data sharing:
synchronization
The process of coordinating the behavior of two or more processes, which may be running on different processors.
lock
A synchronization device that allows access to data to only one processor at a time.
Distributed Memory Multiprocessors
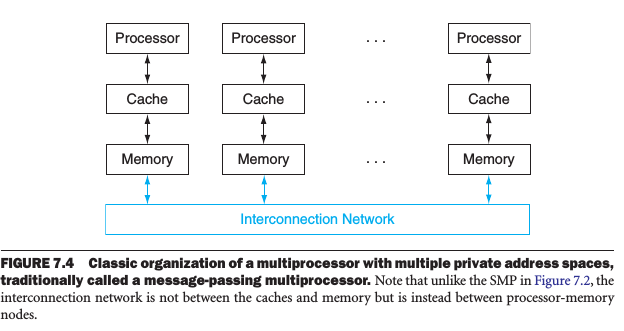
There were several attempts to build high-performance computers based on high-performance message-passing networks, while they were all too expensive than using LAN.
A weakness of separate memories for user memory turns into a strength in system availability.
- It's easier to replace a machine without bringing down the system in a cluster than in an SMP.
- It's easier to expand the system without bringing down the application that runs on top of the cluster.
Lower cost, high availability, improved power efficiency, and rapid, incremental expandability make clusters attractive to service providers for the Word Wide Web.
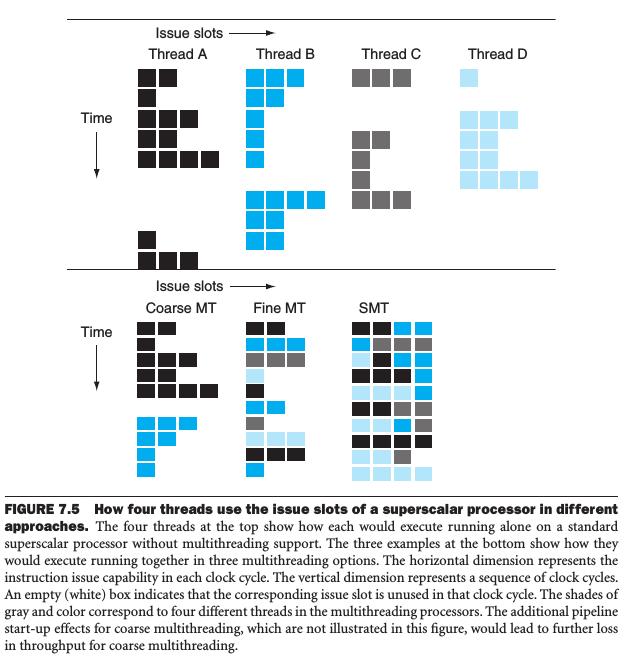
Hardware Multithreading
hardware multithreading
Increasing utilization of a processor by switching to annoher thread when one thread is stalled. To permit this, we must duplicate the independent state. For example, each thread would have a separate copy of the register file and the PC.
There are two main approaches to hardware multithreading.
-
Fine-grained multithreading A version of hardware multithreading that suggests switching between threads after every instruction.
Hiding the throughput losses that arise from both short and long stalls; while slows down the execution of the individual threads.
-
Coarse-grained multithreading A version of hardware multithreading that suggests switching between threads onlly after significant events, such as a cache miss.
Relieves the need to have thread switching be essentially free and is much less likely to slow down the execution of an individual thread; while it's limited in its ability to overcome throughput losses, especially from shorter stalls, since thread switch requires pipeline be emptied or frozen (pipeline start-up cost).
-
Simultaneous multithreading (SMT) A version of multithreading that lowers the cost of multithreading by utilizing the resources neede for multiple issue, dynamically schedule microarchitecture.
本文采用 知识共享署名 4.0 国际许可协议(CC-BY 4.0)进行许可,转载注明来源即可: https://harttle.land/2014/03/01/computer-design-multicore.html。如有疏漏、谬误、侵权请通过评论或 邮件 指出。
